National Hemophilia Foundation (NHF) - Posters
Analysis of Bleeding and Treatment Patterns in Children and Adolescents before and after Von Willebrand Disease Diagnosis Using Data from a US Medical Claims Database |
|
|
|
|
Objectives:
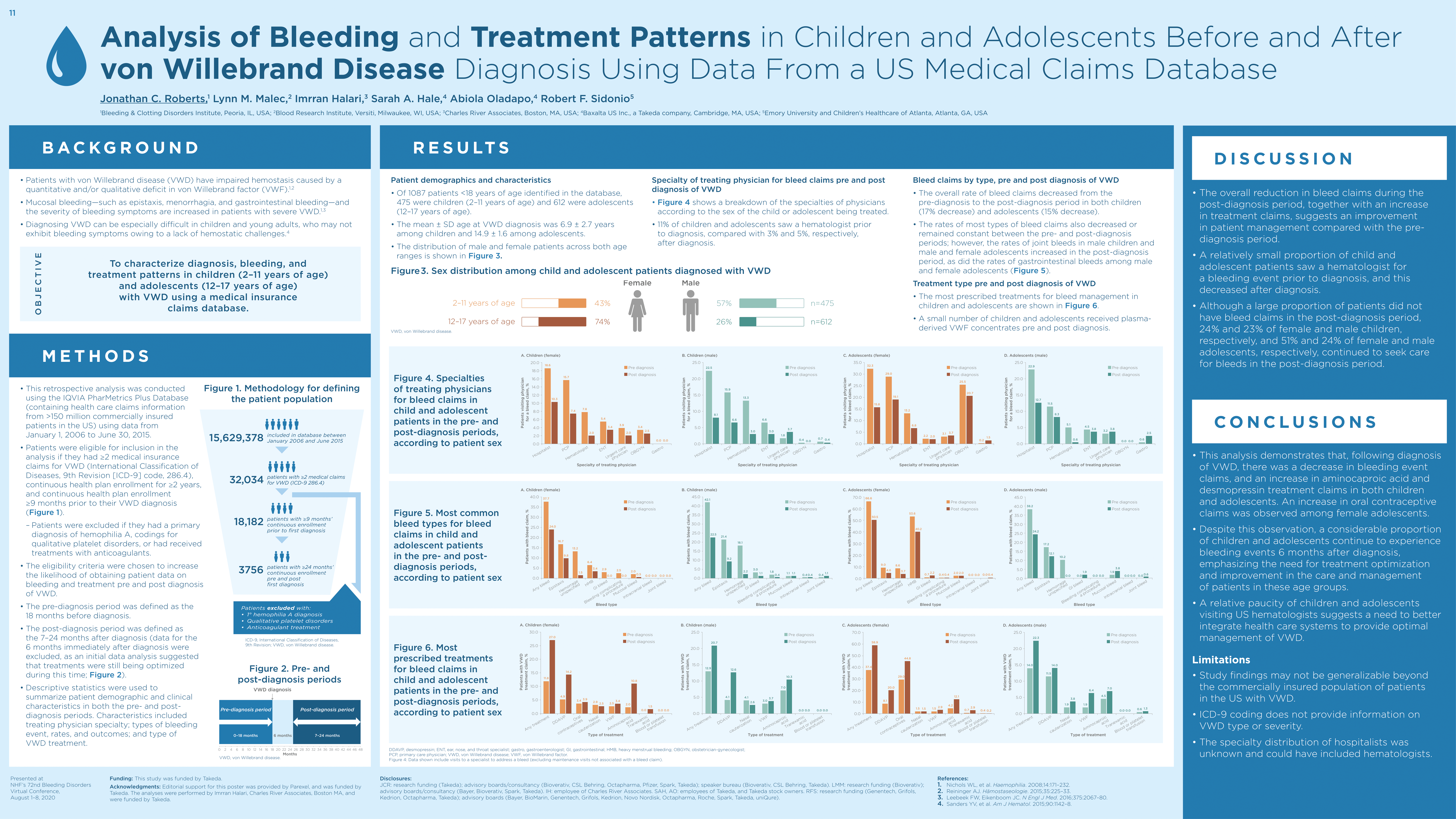
Von Willebrand disease (VWD) is the most common bleeding disorder in children and adolescents. Its varied clinical presentation contributes to challenges and delays in diagnosis and management. We characterized diagnosis, bleeding, and treatment patterns in children (2-11yrs) and adolescents (12-17yrs) with VWD.
Methods:
This retrospective database analysis utilized data from IQVIA PharMetrics Plus Database of medical insurance claims for VWD patients (ICD-9 286.4) from 01/01/2006 to 06/30/2015. Patients included had ?2 medical claims for VWD and continuous enrollment for ?2 years, to ensure higher likelihood of definitive VWD diagnosis, before/after their 1st VWD claim. Pre-diagnosis period included 18mos of data before diagnosis. Post-diagnosis period included 7-24mos post-diagnosis data. Data from the first 6-month post-diagnosis period were excluded due to data variability, suggestive of treatment optimization. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize patient demographic/clinical characteristics, including types of bleeding episode (BE), rates, outcomes; treating physician specialty; and type of VWD treatment, in both pre-/post-diagnosis periods.
Results:
475/1087 patients identified were children (43% female; mean age at diagnosis 6.9yrs; 612 were adolescents (74% female; mean age at diagnosis 14.9yrs). The top 3 treating physician specialties seen by children in the pre-/postdiagnosis periods, respectively, were hospitalists (21%/9%), primary care physicians (16%/7%), and hematologists (11%/3%). Adolescents were mostly seen by hospitalists (30%/15%), primary care physicians (25%/16%), and obstetrician gynecologists (19%/15%). 11% of children and adolescents saw a hematologist prior to diagnosis, compared with 3% and 5%, respectively, post-diagnosis. A 17%/15% decrease in bleed claims in the pre-/post-diagnosis period was observed among children (40%/23%) and adolescents (59%/44%), respectively. The most common type of BE among children in the pre-/post-diagnosis periods was epistaxis (19%/10%). Heavy menstrual bleeding was the most common BE among adolescents in both the pre-/post-diagnosis periods (40%/30%; in females 54%/40%). Epistaxis was the second most common BE among adolescents in both the pre-/post-diagnosis periods (11%/7%), and in females (9%/5%), but highest among males (17%/12%). Overall, VWD-related treatment claims increased between the pre-/post-diagnosis periods for both children (12%/23%) and adolescents (31%/50%). The most prescribed treatments for bleed management in children were aminocaproic acid (ACA), desmopressin (DDAVP) and nasal cauterization (pre-diagnosis: 5%, 4% and 4%, respectively; post-diagnosis: 11%, 13% and 3%, respectively). For adolescents, the most prescribed treatments, pre- and post-diagnosis respectively, were oral contraceptives (22% and 33%, DDAVP (9% and 19%) and ACA (4% and 11%).
Conclusions:
This analysis demonstrates a decrease in BE claims following VWD diagnosis and a rise in ACA and DDAVP treatment claims in both children and adolescents, and in oral contraceptive claims among female adolescents. Nevertheless, a considerable proportion of children and adolescents continue to experience BEs 6mos post-diagnosis. This emphasizes the need for treatment optimization and improvement in care and management of patients in these age groups.



